[Lc]面试题57_II和为s的连续正数序列
Contents
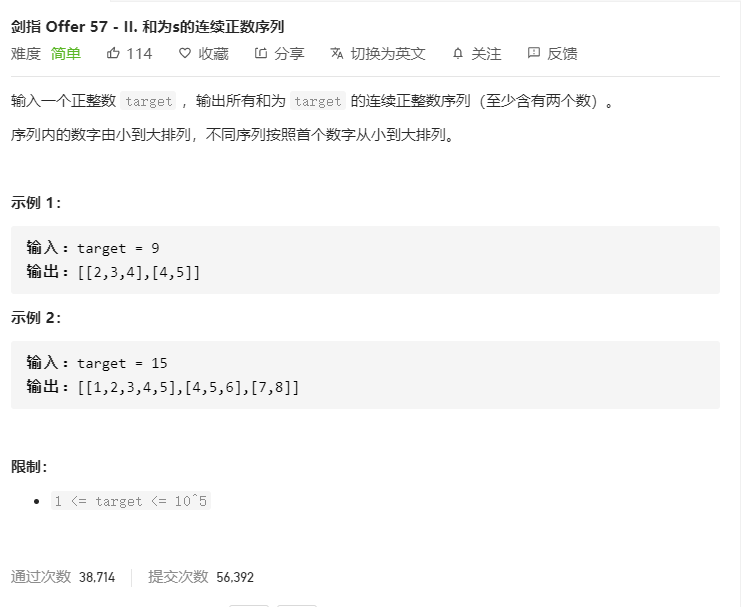
题目
题解
1. 暴力法
挨个计算所有数组的和,时间复杂度太高
- 时间复杂度: $O(n^{2})$
- 空间复杂度: $O(1)$
2. 滑动窗口法
看注释吧,不太难,证明可以看题解
- 时间复杂度: $O(n)$
- 空间复杂度: $O(1)$
class Solution {//三个方法。1.滑动窗口
public:
vector<vector<int>> findContinuousSequence(int target) {
//左闭右开区间,起初sum为0
int left = 1, right = 1;
int sum = 0;
vector<vector<int>> res;
//!!注意这个终止条件
while(right <= target / 2 + 2){
//sum小于target右边界右移
if(sum < target){
sum += right;
right++;
//sum大于target左边界右移
}else if(sum > target){
sum -= left;
left++;
//sum等于target存结果,并左边界左移
}else{
vector<int> arr;
for(int i = left; i < right; ++i) arr.push_back(i);
res.push_back(arr);
sum -= left;
left++;
}
}
return res;
}
};
3. 等差数列通项公式法
来自erick_chen。这个方法很牛逼,理解起来更容易一点
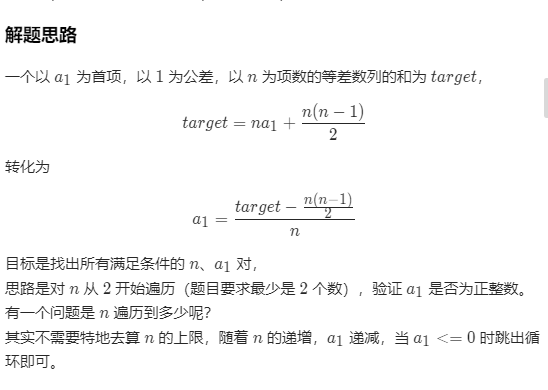
注意几个点:
- n从2开始,因为题目要求数组至少有两个数
- 借鉴题解2,其实n到不了target+1,在分子小于0的时候循环就停止了
- 随着n增加,tmp和a1都递减
- 只有tmp/n为正整数的时候,该结果才有效
- 注意res要从前面插入结果,否则其数列顺序和结果是相反的
- 时间复杂度: $O(n)$
- 空间复杂度: $O(1)$
class Solution {//三个方法。2.等差数列通项公式法
public:
vector<vector<int>> findContinuousSequence(int target) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
for(int n=2; n < target + 1; ++n){
int tmp = target - n * (n - 1) / 2;
if(tmp < 1) break;
if(tmp % n == 0){
int a1 = tmp / n;
vector<int> arr;
for(int i = a1; i <= a1 + n - 1; ++i) arr.push_back(i);
res.insert(res.begin(), arr);
}
}
return res;
}
};
4. 求根公式法
和3的思路类似,也是用等差数列的思想,但是是用求根公式求解,而且会有复数情况,个人感觉理解起来比较困难
- 时间复杂度: $O(n)$
- 空间复杂度: $O(1)$
占坑
Author ChrisHRZ
LastMod 2020-06-26